An overview of the RTLS location technology from AiRISTA
AiRISTA has an active R&D lab where a range of technologies, including Airista Flow solutions and RTLS location technology solutions, are put to the test. Some of these technologies are productized and described below. Others, like LoRa and UWB, are evaluated and a design is created in case the market dictates a shift in that direction. This is one in a series of blogs that will eventually explore the pros & cons of each technology and examples of use cases
Passive RFID

Passive RFID systems consist of tags and readers. The reader is a networking device similar to an access point that emits a directed radio signal in the UHF frequency. The tag is a simple device consisting of a chip and an antenna. The antenna absorbs the UHF energy from the reader and reflects that energy back to the reader with the chip’s unique identifier.
BLE Proximity

Like passive RFID, BLE proximity uses a reader device to detect a signal emitted by a BLE tag. The tag, in this case, is battery powered which provides greater range than a passive tag. The strength of the tag’s BLE signal is inversely proportional to the distance. Changing the characteristics of the reader’s antenna, the field of detection can be tuned for wider or narrower fields of capture. BLE technology is particularly effective for tracking and managing assets, providing real-time location insights, and improving monitoring and resource optimization. BLE technology also supports the customization of workflows related to asset management and safety protocols. Pictured to the left is the AiRISTA A1 BLE tag.
Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI)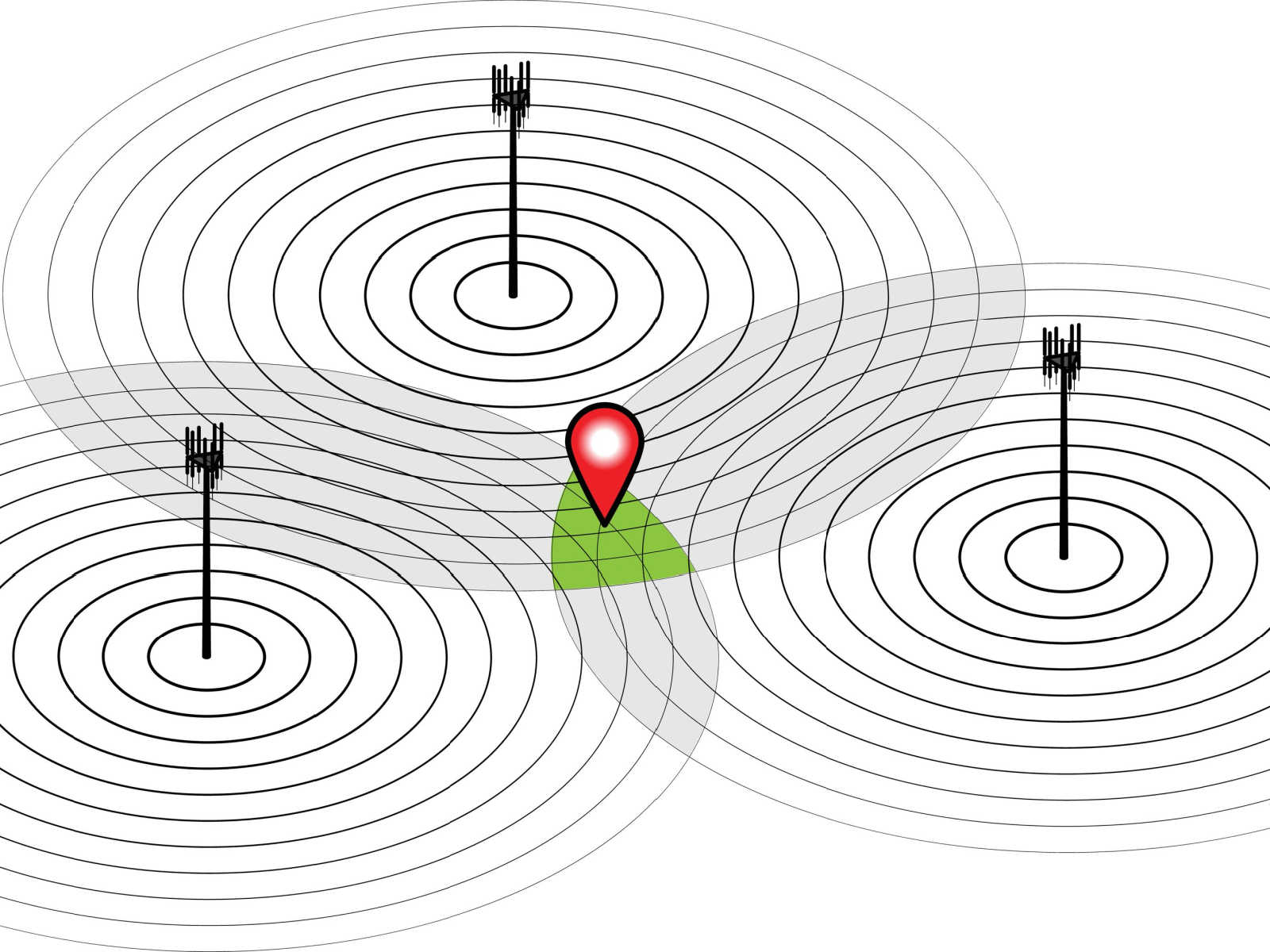
Active RFID tags (aka ) use a battery to produce a wireless signal. Wi-Fi and Bluetooth® Low Energy (BLE) are typical radios and these signals are detected by receivers (typically your existing access points). The receiver records the strength of the received signal and compares that value with other access points receiving the same signal. Knowing the location of each access point and the received signal strength, the tag’s location can be determined using trilateration – the stronger the signal, the closer the tag is to the access point. This technology enhances visibility by providing real-time insights into asset location and status, positioning AiRISTA as a leader in the industry, thereby improving organizational efficiency and safety.
BLE Angle of Arrival & Angle of Departure (AoA & AoD)
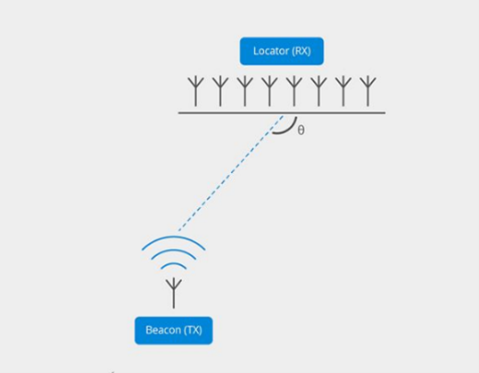
Rather than using relative signal strength, AoA uses a receiver (reader) that uses the “angle” of the BLE signal as it arrives from the tag. The angle is compared among a series of micro-antenna precisely located on the antenna substrate. The minute differences between the micro-antenna trace back vectors that converge on the location. Note, that “angle” is an easy way to conceptualize the process, but it’s actually the difference in the phase of the arriving signal).
AoD uses the same principles but reverses the model where the item being tracked is calculating location based on the angle of the departing signal from 2 or more fixed beacons.
BLE High Accuracy Distance Measurement (HADM)
HADM uses very simple infrastructure to achieve an accuracy of 10’s of centimeters. As a signal travels from transmitter to receiver and back, the signal’s phase shifts proportionate to the distance. The magnitude of the phase shift is used to calculate the distance. To remove the effect of multipath (reflected signals that act like echoes), frequency hopping is used to compare phase shifts at multiple frequencies. AiRISTA expects fully productized solutions in early 2023.

Global Positioning System (GPS)
Global positioning systems use a series of 30+ low-orbit satellites which transmit their precise location to receivers on earth. When a tag with a GPS receiver detects 4 or more satellites, the receiver uses trilateration to calculate its longitude and latitude based on its distance from each satellite. As with RSSI, accuracy increases with the more satellites the tag recognizes.
Although the tag only receives GPS signals (the tag does not transmit), it is nonetheless power-hungry. If they don’t have a constant power source, tags using batteries can conserve power by shutting down when GPS tracking is not needed.
Pictured below is the AiRISTA A67 tag asset tag for indoor and outdoor tracking using GPS. AiRISTA Flow’s solutions are applied in various industries, including healthcare, to enhance asset visibility and meet regulatory requirements.

Batteryless BLE
Similar to passive RFID, batteryless BLE uses ambient radio energy to power the tag. Places like work, home, or the shopping mall are constantly bombarded by radio devices that provide a rich source of power. The batteryless tag contains a chip and antennae that reflect this harvested energy in the form of a unique identifier in the BLE spectrum unlike traditional RTLS systems which require specific devices like access points to receive the tag’s signal, common devices like your personal cell phone or an Echo Dot can detect the tag and pass along its ID over legacy networks like your phone’s cellular service or your surrounding Wi-Fi.
AiRISTA is evaluating the technology in its R&D labs and is excited about its potential, but has no product based on batteryless BLE at this time. However, the integration and compatibility of the CMX Detect and locate module with various Airista Flow products remain a topic of interest, especially in terms of Wi-Fi location services. Customers can easily add AiRISTA’s batteryless BLE tags to their virtual shopping cart for purchase, streamlining the buying process. To find out more about AiRISTA RTLS technologies download the FREE white paper that explores the pros & cons as well as example use cases.